Accurately annotating cell types is a prerequisite for obtaining biologically robust results from single-cell transcriptomic data. To gain confidence in the analysis process, we curate compendia of single-cell studies from selected areas and combine multiple studies into a single statistical framework. This harmonization and statistical alignment of studies into atlases and cell-type references requires specialized expertise, which we have developed over the years. The Immunai single-cell curation team recently established a harmonized single nuclei atlas of the human brain.
Summary of the Immunai human brain atlas
The following 14 single-nuclei public studies (using GENEVESTIGATOR® IDS) were curated and harmonised: HS-04386, HS-04340, HS-03878, HS-03909, HS-03685, HS-04357, HS-04337, HS-04329, HS-03964, HS-03910, HS-03271, HS-03907, HS-03906, HS-03905. This resulted in a harmonized neuroscience atlas comprising:
- Total cells harmonized: 1,336,998 cells
- Unchanged cell type annotation: 493,311 cells
- Changed cell type annotation (mainly deeper granularity): 826,248 cells
- Removed: 17,439 cells
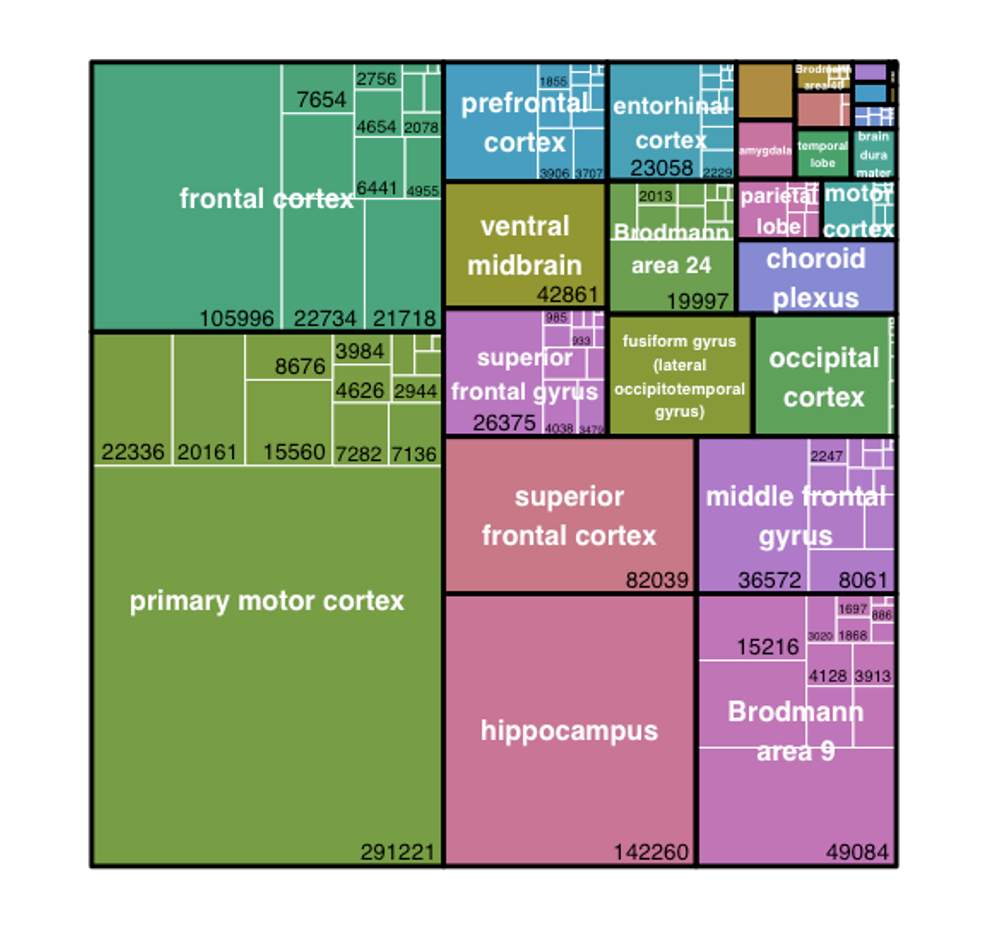
Highlights of harmonization outcome:
- Total of 98 identified cell types
- 44 newly annotated subclasses of inhibitory neurons based on enriched genes
- 18 newly annotated subclasses of excitatory neurons based on enriched genes
- Improved neuron identification through assignment of cortical layers into anatomy section
- Improved and more robust annotations of intermediate stages of oligodendroglial lineage (two types of newly-formed oligodendrocyte and two types of myelin-forming oligodendrocytes)
- Discrimination of dural and arachnoidal fibroblast and identification of ectoderm barrier epithelium cell in arachnoidea (a.k.a. arachnoid barrier cells)
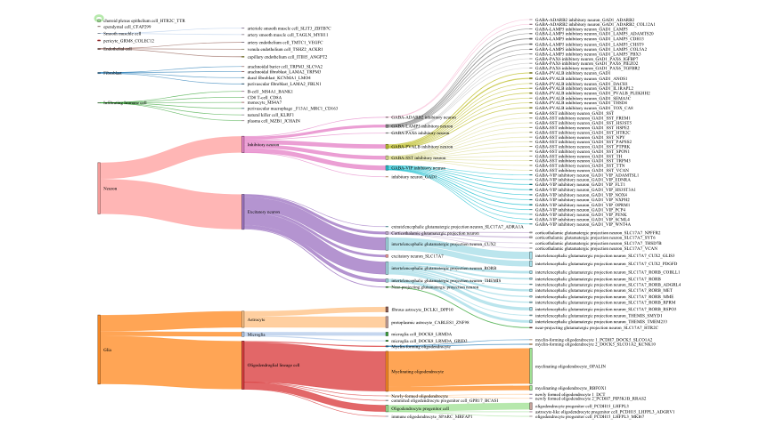
Examples of how the Immunai brain atlas can be used
- Identification of disease-specific cell types and biomarkers: identify cell types and corresponding gene expression patterns that are specific to a particular disease or condition.
- Understanding the molecular basis of developmental processes: understand the molecular mechanisms that drive developmental processes, such as organogenesis and tissue differentiation.
- Drug target discovery: identify new drug targets by identifying cell types and gene expression patterns that are involved in disease progression.
- Drug candidate validation: validate the efficacy of drug candidates in preclinical models.
To arrange a more detailed presentation of our brain atlas, please contact sales@nebion.com.